Cobra¶
The Cobra Line Follower provides an array of line IR reflective sensors to be used for detecting a line. The Cobra uses four QRE1113 sensors for detecting the line.
Function |
Min |
Nom |
Max |
|---|---|---|---|
Input Voltage |
3.3VDC |
5VDC |
5VDC |
Current |
25mA |
70mA |
100mA |
Sensing Distance |
2mm |
3mm |
— |
Analog Module¶
To plug the Cobra into the VMXpi the analog module is required.
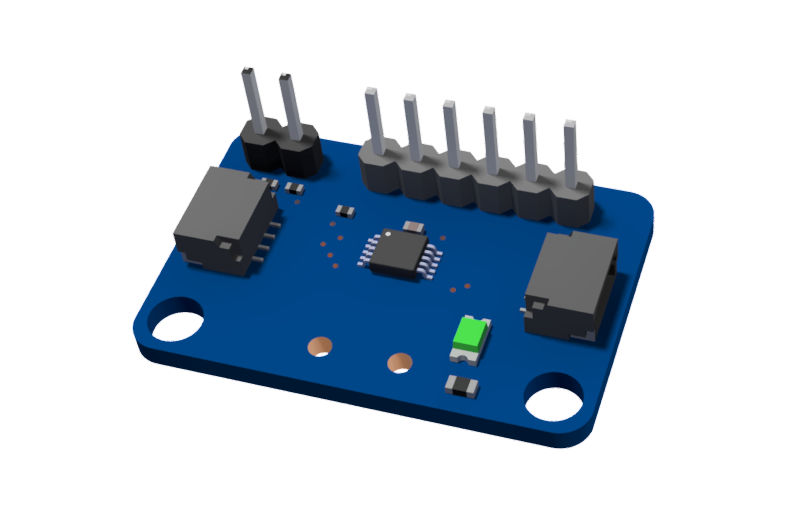
The Cobra will plug directly into the analog module. The module will then use the provided JST SH to JST GH cable to connect to the i2c port on the VMXpi.
Programming the Cobra¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | //import the Cobra Library import com.studica.frc.Cobra; //Create the Cobra Object private Cobra cobra; //Constuct a new instance cobra = new Cobra(); // or if sensor is using 3.3V cobra = new Cobra(3.3F); //Can then use these accssors to get data cobra.getVoltage(channel); //returns a float cobra.getRawValue(channel); //returns a double |
The accessor methods will output either the voltage (0 - 5V) or the raw ADC value (0 - 2047).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | //Include the Cobra Library #include "studica/Cobra.h" //Constructors studica::Cobra cobra{}; // or if sensor is using 3.3V studica::Cobra cobra{3.3F}; //Use these to access data cobra.GetVoltage(channel); //returns a float cobra.GetRawValue(channel); //returns a double |
The accessor functions will output either the voltage (0 - 5V) or the raw ADC value (0 - 2047).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | //Include the Cobra Library #include "Cobra_ros.h" double channel_1_V; // Returns the channel 1 voltage value reported by the Cobra sensor void c1_v_callback(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& msg) { channel_1_V = msg->data; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { system("/usr/local/frc/bin/frcKillRobot.sh"); //Terminal call to kill the robot manager used for WPILib before running the executable. ros::init(argc, argv, "cobra_node"); /** * Constructor * Cobra's ros threads (publishers and services) will run asynchronously in the background */ ros::NodeHandle nh; //internal reference to the ROS node that the program will use to interact with the ROS system VMXPi vmx(true, (uint8_t)50); //realtime bool and the update rate to use for the VMXPi AHRS/IMU interface, default is 50hz within a valid range of 4-200Hz ros::Subscriber c1_v_sub; CobraROS cobra(&nh, &vmx); //default device address is 0x48 and default voltage is 5.0F // or can use CobraROS cobra(&nh, &vmx, deviceAddress); // or if sensor is using 3.3V, refVoltage(3.3F) CobraROS cobra(&nh, &vmx, deviceAddress, refVoltage); // Use these to directly access data float voltage = cobra.GetVoltage(channel); //returns a float int raw_cobra = cobra.GetRawValue(channel); //returns an int // Subscribing to a Cobra voltage topic to access the voltage data c1_v_sub = nh.subscribe("cobra/c1/voltage", 1, c1_v_callback); ros::spin(); //ros::spin() will enter a loop, pumping callbacks to obtain the latest sensor data return 0; } |
The accessor functions will output either the voltage (0 - 5V) or the raw ADC value (0 - 2047).
Important
Subscribe to Cobra topics to access the data being published and write callbacks to pass messages between various processes.
Note
Calling the frcKillRobot.sh script is necessary since the VMXPi HAL uses the pigpio library, which unfortunately can only be used in one process. Thus, everything that interfaces with the VMXPi must be run on the same executable. For more information on programming with ROS, refer to: ROS Tutorials.